Description
This article provides step-by-step instructions on how to set up continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) to Netlify for static site deployments using Github. Readers will learn how to optimize their deployment pipeline for maximum efficiency, streamline their workflow and reduce the risk of errors.
Like this website? It was built with Amazing Hugo Shortcodes
I. Introduction
In today’s fast-paced software development landscape, Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) have become crucial for ensuring high-quality software releases at a rapid pace. Netlify is a popular cloud-based hosting platform that provides an easy way to deploy static sites. By automating the deployment process with CI/CD, developers can focus on writing code and delivering features rather than manually deploying changes. In this article, we will explore how to set up CI/CD to Netlify for static site deployments. We will discuss the benefits of this approach, and provide a step-by-step guide for integrating Github with Netlify for a streamlined deployment process.
For this article, I will be using a Hugo static site that I used to build a personal portfolio and blog for my audience to demonstrate the CI/CD pipeline. Please take a close look at the Github Repository for the same.

II. Setting Up a Netlify Account
In order to set up CI/CD to Netlify for static site deployment, you will need to create a Netlify account. If you already have a Netlify account, you can skip this section and move on to the next section.
Tired of managing hundreds of tabs? Discover how to Stay Organized in Chrome
Netlify is a cloud-based service that offers continuous deployment, hosting, and serverless backend functionality for static websites. With Netlify, you can easily deploy and manage static sites with automatic CI/CD capabilities.
-
Creating a Netlify account To create a Netlify account, go to netlify.com and click the “Sign up” button in the upper right corner of the page. You can sign up with your GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket account or by using your email address.
-
Setting up a new site on Netlify Once you have created a Netlify account, you can set up a new site by clicking the “New site from Git” button on the Netlify dashboard. From there, you will need to select the Git provider that hosts your repository. In this case, we will be using GitHub.
-
Linking the site to a GitHub repository After selecting GitHub as the Git provider, Netlify will prompt you to authenticate with your GitHub account. Once authenticated, you will be able to select the repository that you want to link to your Netlify site. After selecting the repository, you will be presented with a list of configuration options for your site.
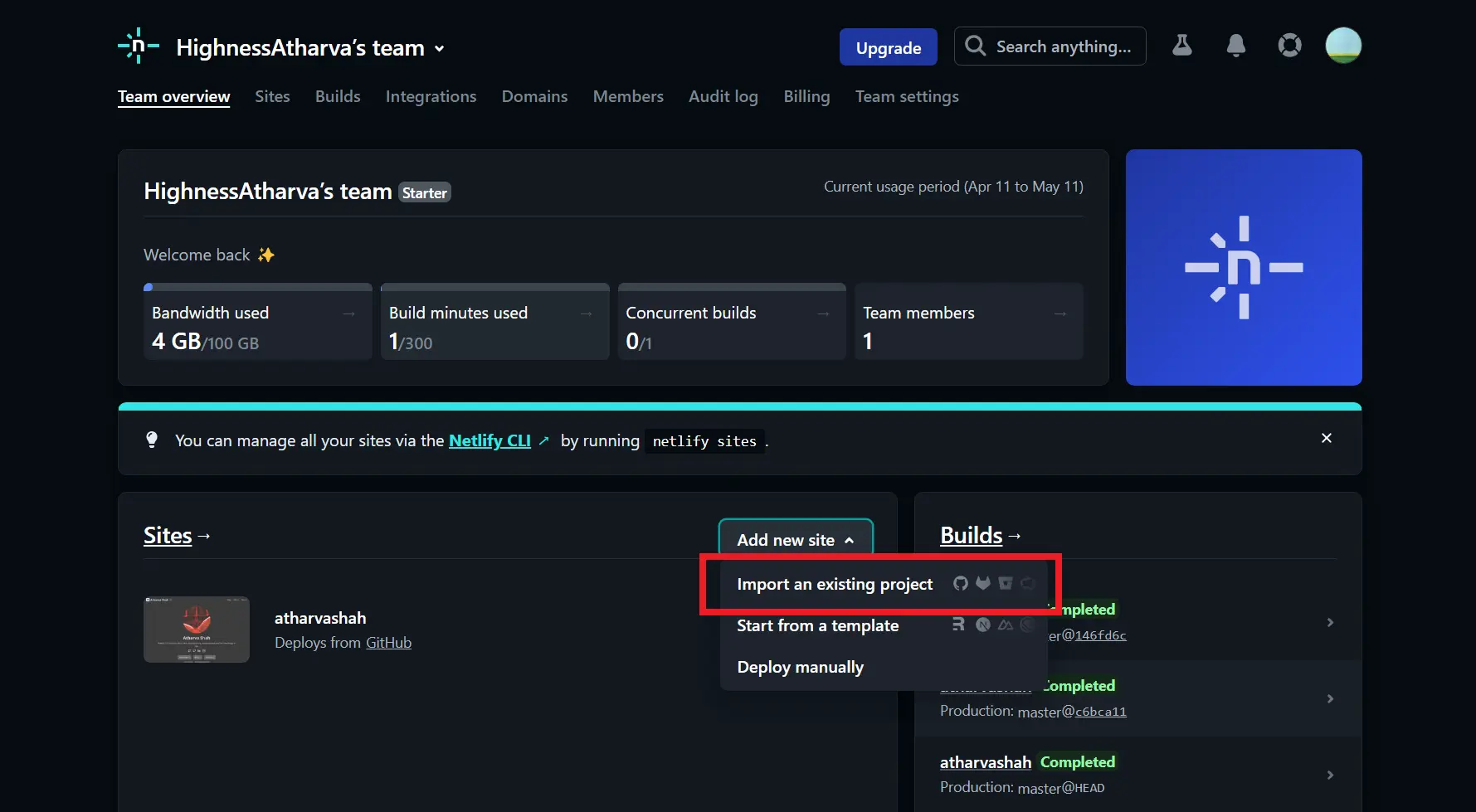
In the next section, we will discuss how to configure your GitHub repository for automatic deployments to Netlify.
III. Setting Up CI/CD to Netlify
CI/CD (Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment) is a process that automates the building, testing, and deploying of code changes. By setting up CI/CD to Netlify for your static site via Github, you can ensure that your code changes are automatically tested, built, and deployed to your production site every time you make a commit.
Netlify provides a simple and intuitive way to configure CI/CD for your static site. Here’s how to do it:
Configuring the Build Settings on Netlify
Before you can set up CI/CD to Netlify, you need to configure the build settings on Netlify. Netlify uses build plugins to configure the build process. Build plugins are reusable pieces of code that can be shared across different sites and projects.
To configure the build settings, follow these steps:
- Go to your site’s settings page on Netlify.
- Click on the “Build & deploy” tab.
- Scroll down to the “Build plugins” section.
- Click the “Add build plugin” button.
- Select the “Build Command” plugin.
- In the “Command” field, enter the build command for your static site. For example, if you’re using Jekyll, the build command would be “jekyll build”. If you’re using Hugo, the build command would be “hugo”.
- Click “Save”.
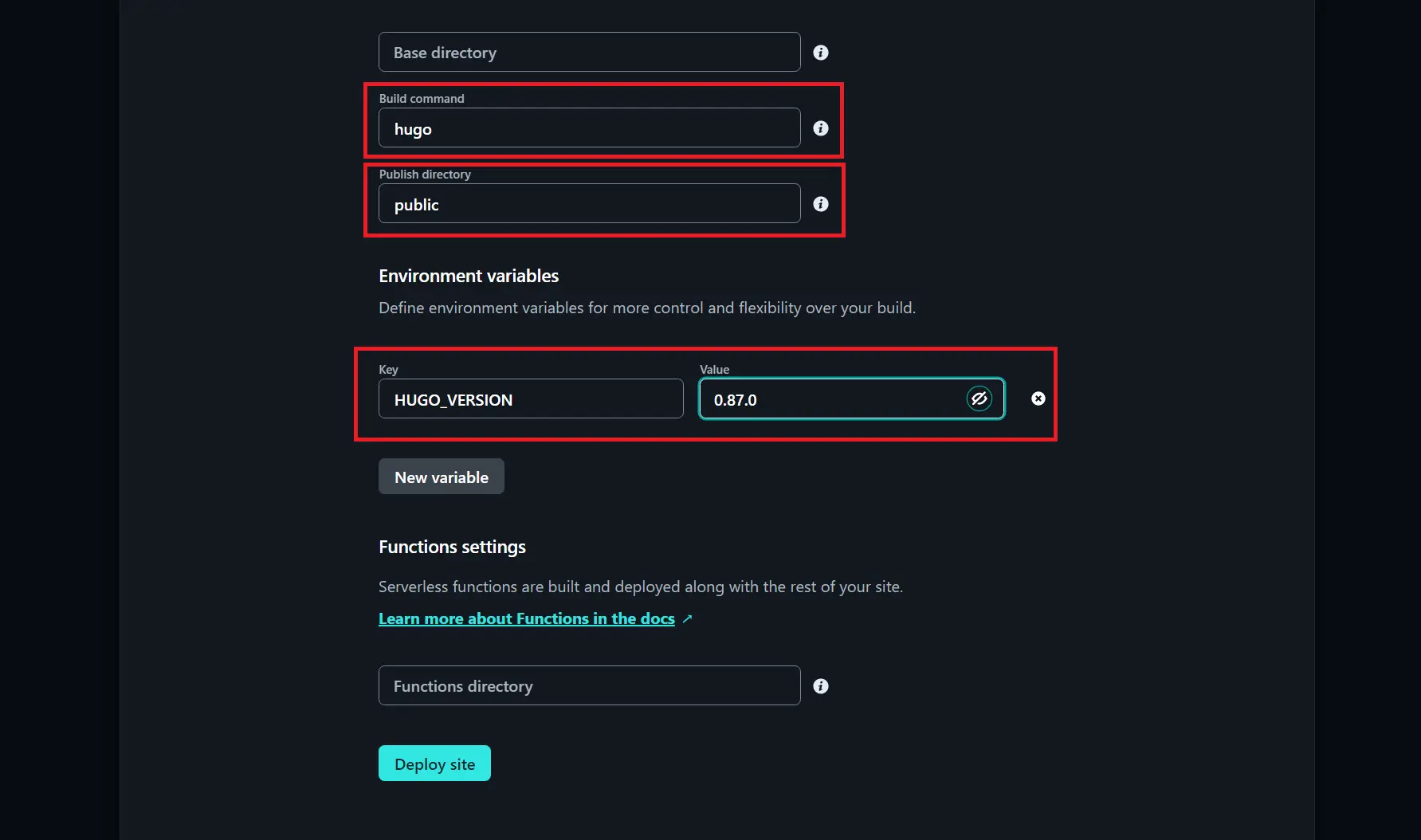
Configuring the Deployment Settings on Netlify
Once you’ve configured the build settings, you need to configure the deployment settings on Netlify. Netlify provides several deployment options, including manual deploys, continuous deployment, and branch deploys.
To configure the deployment settings, follow these steps:
- Go to your site’s settings page on Netlify.
- Click on the “Build & deploy” tab.
- Scroll down to the “Deploy notifications” section.
- Click the “Add notification” button.
- Select the deployment method you want to use. For example, if you want to use continuous deployment, select “GitHub”. If you want to use manual deploys, select “Manual deploys”.
- Follow the prompts to authenticate with GitHub and select the repository and branch you want to deploy.
That’s it! Netlify will now automatically build and deploy your static site every time you push a new commit to the linked GitHub repository. If there are any errors in the build process, Netlify will notify you via email or Slack.
IV. Setting Up CI/CD with Github Actions
In the previous section, we set up the basic CI/CD configuration on Netlify. However, we haven’t automated the process yet. In this section, we’ll use Github Actions to automate our CI/CD process.
Introduction to Github Actions
Github Actions is a powerful tool that allows you to automate tasks directly in your Github repository. It works by defining workflows as code that are triggered by specific events such as push, pull request, or cron schedules. A workflow is made up of one or more jobs that can be run on different operating systems and virtual environments. Each job is made up of one or more steps that are executed in sequence. Steps are individual tasks, such as building and testing your code or deploying it to a server.
Github Actions provides a wide range of pre-built actions, which are individual tasks that can be used within your workflows. These actions are reusable, making it easy to build custom workflows without having to write much code.
Creating a Github Actions Workflow for the Static Site
To create a workflow, we need to create a YAML file in the .github/workflows directory in our Github repository. This file defines the workflow and its associated jobs and steps.
First, we need to define the event that triggers the workflow. In our case, we want the workflow to be triggered whenever changes are pushed to the main branch. Here’s an example YAML configuration that achieves this:
codename: Deploy to Netlify
on:
push:
branches:
- main
Next, we need to define the jobs that make up the workflow. In our case, we only need one job, which will build and deploy our site. Here’s an example YAML configuration for the job:
codejobs:
build-and-deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm install
- name: Build site
run: npm run build
- name: Deploy site to Netlify
uses: nwtgck/actions-netlify@v1
with:
publish-dir: ./dist
production-command: echo 'No production command required for static site deployment'
env:
NETLIFY_AUTH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.NETLIFY_AUTH_TOKEN }}
NETLIFY_SITE_ID: ${{ secrets.NETLIFY_SITE_ID }}
Let’s go through each step of the job:
runs-on: ubuntu-latestspecifies that the job will run on a Ubuntu environment.actions/checkout@v2checks out the code from Github so that it can be built and deployed.npm installinstalls the dependencies required to build the site.npm run buildbuilds the site using the build command specified in ourpackage.jsonfile.nwtgck/actions-netlify@v1is an action that deploys our site to Netlify.publish-dir: ./distspecifies the directory containing our built site.production-command: echo 'No production command required for static site deployment'is not required for static site deployments.NETLIFY_AUTH_TOKENandNETLIFY_SITE_IDare environment variables that contain the API key and site ID for our Netlify account. These are passed in as secrets in the Github repository settings.
Once we’ve created this YAML configuration file, Github Actions will automatically detect it and run it whenever changes are pushed to the main branch.
Configuring the Workflow to Deploy to Netlify
Before we can deploy to Netlify using Github Actions, we need to configure the workflow to tell it where to deploy and how to authenticate with Netlify.
First, we need to set up an access token in Netlify to allow Github to deploy to our site. To do this, navigate to the Netlify dashboard and click on the site we want to deploy to. Then, click on the “Settings” tab and scroll down to the “Access tokens” section. Click the “New access token” button, and give it a name that reflects its use, such as “Github Actions deployment.”
Next, select the desired permissions for the token. For deployment purposes, we only need to grant the “deploy” permission. Once we have selected the “deploy” permission, click the “Generate token” button at the bottom of the page. Netlify will generate a new access token, which we need to copy and store safely in our Github repository’s secrets.
To add the Netlify access token to our repository’s secrets, we need to navigate to the repository’s “Settings” tab and click on “Secrets” on the left-hand side. Then, click the “New repository secret” button, and enter “NETLIFY_AUTH_TOKEN” as the name of the secret. In the “Value” field, paste the access token we just copied from Netlify. Finally, click the “Add secret” button to save the token.
Now that we have our access token set up and safely stored, we can add the deployment step to our Github Actions workflow. To do this, we need to modify the workflow YAML file we created earlier. We will add a new step at the end of the workflow to deploy the site to Netlify.
Here’s an example deployment step that we can add to our YAML file:
codename: Deploy to Netlify
uses: nwtgck/actions-netlify@v1
with:
NETLIFY_AUTH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.NETLIFY_AUTH_TOKEN }}
NETLIFY_SITE_ID: your_site_id
DIR_TO_UPLOAD: your_dir_to_upload
This step uses the “nwtgck/actions-netlify” Github Action, which simplifies the deployment process to Netlify. We need to provide the access token we just created, along with the site ID and directory we want to upload.
To find the site ID, navigate to the site’s “Settings” tab in the Netlify dashboard and scroll down to the “Site details” section. The site ID will be listed under the site name.
Finally, we need to specify the directory we want to upload to Netlify. This directory should contain the built version of our static site. The directory can be specified using the “DIR_TO_UPLOAD” parameter in the YAML file.
Once we have added the deployment step to the workflow YAML file, we can commit and push the changes to Github. Github Actions will automatically run the workflow when changes are pushed to the repository, which will trigger the build and deployment process to Netlify.
With everything set up, we can now sit back and watch as our site is automatically built and deployed to Netlify every time we push changes to Github. This is a powerful workflow that simplifies the deployment process and frees up time to focus on developing our site.
V. Best Practices for CI/CD with Netlify and Github
Setting up CI/CD to Netlify via Github is a powerful combination that allows for seamless deployments of static sites. However, there are some best practices that can help optimize the process and ensure smooth operations. Here are some tips for optimizing your CI/CD pipeline and managing your Github repository and Netlify site:
- Regularly test your deployment process: It’s important to test your deployment process regularly to catch issues early on. You can do this by creating a test branch and testing the deployment process on a separate staging site before deploying to production.
- Use version control effectively: Make sure to use version control effectively by using clear commit messages, creating meaningful branch names, and enforcing code reviews. This helps keep your codebase organized and makes it easier to roll back changes if needed.
- Use environment variables: Netlify allows for the use of environment variables to keep sensitive information secure, such as API keys or access tokens. Make sure to use these variables and not hardcode any sensitive information into your deployment scripts.
- Optimize build time: Netlify has a limit of 15 minutes for the build time of each deployment. If your build time exceeds this limit, you may run into issues. To optimize build time, make sure to only install necessary dependencies and remove any unnecessary files or processes.
- Use caching: Caching is a great way to speed up build times and reduce the number of API calls needed. Netlify supports caching of dependencies, and Github Actions supports caching of build artifacts.
- Monitor your deployments: Keep an eye on your deployments to ensure they are successful and catch any errors early on. You can set up notifications to alert you of failed deployments or use tools like Sentry or New Relic for error monitoring.
- Backup your data: Regularly backup your data to prevent data loss. Netlify provides built-in backup functionality, but it’s always a good idea to have an offsite backup as well.
By following these best practices, you can optimize your CI/CD pipeline and ensure smooth deployments of your static site to Netlify. Remember to test regularly, use version control effectively, keep sensitive information secure with environment variables, optimize build time, use caching, monitor your deployments, and backup your data to prevent data loss.
VI. Troubleshooting CI/CD Issues
Even with the best practices in place, issues can arise during the CI/CD process that can cause headaches for developers. Here are some common issues and troubleshooting steps to help you diagnose and resolve problems with the deployment pipeline.
- Build Fails
One of the most common issues that developers face is a failed build. This can be caused by a number of factors, including incorrect build settings, missing dependencies, or errors in the code. When a build fails, the first step is to check the build logs to identify the source of the problem. Netlify provides detailed logs that can help you diagnose the issue. Once you have identified the problem, you can make the necessary changes to the build settings or code to resolve the issue.
- Deployment Fails
Another common issue is a failed deployment. This can occur if there are errors in the deployment settings or if there are issues with the Netlify API. When a deployment fails, check the deployment logs to identify the source of the problem. If the issue is with the deployment settings, make the necessary changes and try again. If the issue is with the Netlify API, you may need to contact Netlify support for assistance.
- Slow Builds or Deployments
Sometimes, builds or deployments may take longer than expected. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including slow network speeds, large files, or complex code. To resolve this issue, try optimizing your code or reducing the size of your files. You can also consider upgrading to a higher-tier Netlify plan for faster build and deployment speeds.
- Caching Issues
Caching can also cause issues during the CI/CD process. If changes are not reflected in the deployed site, it may be due to caching. To resolve this issue, you can clear the cache in Netlify or disable caching in your browser.
- Authentication Issues
Authentication issues can also cause problems during the CI/CD process. If you are having trouble authenticating with Github or Netlify, double-check your credentials and make sure that you have the necessary permissions to access the repository or site.
VII. Conclusion
In conclusion, setting up CI/CD to Netlify for a static site via Github provides a streamlined approach to deploying code changes. It eliminates the need for manual deployment processes, saves time and increases productivity.
To set up this process, you will need to create a Netlify account, link it to your Github repository, configure the build and deployment settings on Netlify, and create a Github Actions workflow.
In the workflow, you will define the steps to build and deploy the site to Netlify. Github Actions is a powerful tool that allows for a wide range of customization, making it possible to fine-tune the deployment process to your specific needs.
To optimize the pipeline, we recommend implementing best practices such as using Git branches and pull requests, setting up automatic testing, and monitoring the deployment pipeline for errors.
In case of any issues during the CI/CD process, it is important to have a troubleshooting plan in place. This includes diagnosing and resolving issues with the pipeline, using tools such as logs and error messages to determine the root cause of the issue.
Overall, setting up CI/CD to Netlify for a static site is a valuable addition to any development workflow. It simplifies the deployment process and frees up developers’ time to focus on building and improving the site itself. With the steps outlined in this guide, you can easily set up and customize the pipeline to fit your specific needs.
